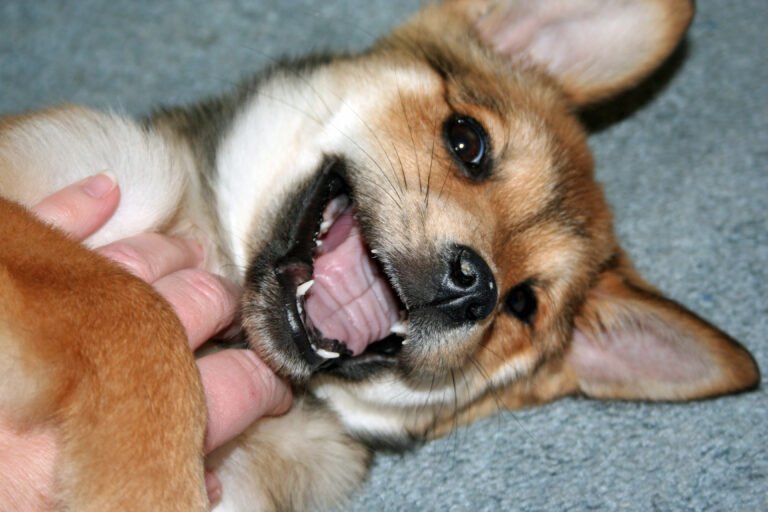
How to Teach My Puppy to Stop Biting: A Complete Guide for New Dog Parents
Welcome to the wonderful world of puppy parenthood! If you’re here, chances are your adorable new furry friend has been treating your hands, arms, and possibly your favorite shoes like their personal chew toys. Don’t worry – you’re not alone in this journey, and more importantly, puppy biting is completely normal behavior that can be successfully managed with the right approach.
Those razor-sharp puppy teeth might feel like tiny daggers, but this phase is actually a crucial part of your pup’s development. Every dog owner faces this challenge, from first-time pet parents to experienced dog lovers welcoming their fourth or fifth companion. The good news? With patience, consistency, and the proven techniques we’ll share in this comprehensive guide, you can teach your puppy to stop biting and develop proper bite inhibition skills.
Throughout this article, we’ll explore why puppies bite, when this behavior typically peaks, and most importantly, how to redirect it into appropriate outlets. Whether you’re dealing with gentle mouthing during playtime or more persistent nipping that’s becoming a concern, we’ve got you covered with expert-backed strategies that work.
Understanding Why Puppies Bite: The Natural Development Process
Before diving into training techniques, it’s essential to understand that puppy biting isn’t aggression – it’s communication and exploration. Young dogs use their mouths the same way human toddlers use their hands to investigate the world around them. This natural behavior serves several important purposes in your puppy’s development.
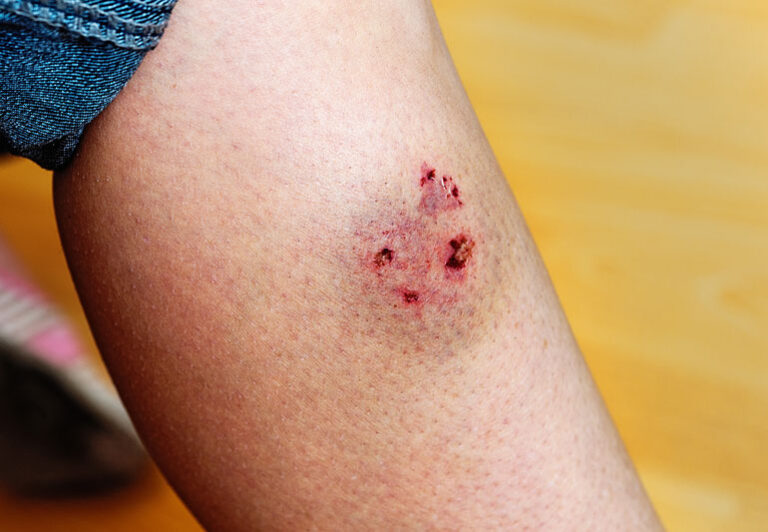
Teething is one of the primary reasons puppies engage in excessive biting and chewing. Just like human babies, puppies experience discomfort as their adult teeth emerge, typically between 3 to 6 months of age. During this period, chewing and biting provide relief from the pressure and pain in their gums. Your puppy isn’t trying to be destructive – they’re simply seeking comfort.
Dr. Sarah Mitchell, Certified Dog Behaviorist: “Puppy biting is a normal part of canine development, similar to how human children explore through touch. The key is teaching appropriate bite inhibition early, as this foundation will serve your dog throughout their entire life. Most puppies naturally begin to reduce biting behavior around 4-5 months of age with proper guidance.”
Social learning also plays a crucial role in biting behavior. In a natural pack setting, puppies learn bite inhibition from their littermates and mother. When a puppy bites too hard during play, their sibling will yelp and stop playing, teaching the biter that excessive force ends the fun. Unfortunately, many puppies are separated from their litters before fully learning these important social cues, making it our responsibility as pet parents to continue this education.
Energy release is another significant factor. Puppies have boundless energy and limited outlets for expression. Biting during play helps them burn off excess energy while engaging their natural hunting and play instincts. Understanding this helps us redirect the behavior rather than simply trying to suppress it.
The Critical Importance of Bite Inhibition Training
Bite inhibition is arguably the most important skill your puppy will ever learn. This concept refers to a dog’s ability to control the force of their bite, essentially teaching them to have a “soft mouth.” Even the most gentle, well-trained adult dogs may find themselves in situations where they might bite – perhaps they’re scared, in pain, or protecting their family. A dog with proper bite inhibition will cause minimal damage in such rare circumstances.
The window for teaching bite inhibition is relatively narrow, making early training crucial. Puppies are most receptive to this learning between 3 to 14 weeks of age, though training can certainly continue beyond this period. The earlier you start, the more effective your training will be.
Kathy Santo, Professional Dog Trainer and AKC Columnist: “Teaching bite inhibition isn’t about stopping all mouthing behavior immediately – it’s about teaching your puppy to control the pressure of their bite. This is a gradual process that builds a foundation of trust and communication between you and your dog.”
Proper bite inhibition training occurs in stages. First, you’ll work on reducing the force of your puppy’s bite, then gradually decrease the frequency of mouthing behavior. This approach ensures your puppy learns both pressure control and appropriate timing for mouth-based interaction.
Proven Methods to Stop Puppy Biting
The Yelp and Withdraw Method
One of the most effective techniques for teaching bite inhibition mimics how puppies naturally learn from their littermates. When your puppy bites too hard during play, immediately let out a high-pitched yelp – similar to how another puppy would react. This sound should be sharp and startling, but not angry or threatening.
Immediately after yelping, withdraw your attention completely. Turn away from your puppy, cross your arms, and ignore them for 30 to 60 seconds. This withdrawal of attention is incredibly powerful for social animals like dogs. Your puppy will quickly learn that hard biting results in the immediate end of fun interaction.
Consistency is crucial with this method. Every family member should respond the same way to inappropriate biting. If one person allows rough play while another doesn’t, your puppy will become confused about what’s acceptable behavior.
Positive Reinforcement and Redirection
While it’s important to discourage inappropriate biting, it’s equally crucial to reward good behavior. Positive reinforcement training focuses on rewarding your puppy when they make good choices, making them more likely to repeat those behaviors.
When your puppy is playing gently or chewing on appropriate toys, immediately praise them with enthusiasm. Use phrases like “good gentle!” or “yes, good toy!” to help them understand what behavior you want to see more of. High-value treats can also reinforce these positive moments.
Dr. Patricia McConnell, Animal Behaviorist: “Redirection is more effective than punishment because it teaches your puppy what TO do, not just what NOT to do. When you redirect biting onto appropriate toys and then praise the behavior, you’re building positive associations with appropriate chewing outlets.”
Redirection should happen the moment you feel teeth on skin. Keep appropriate chew toys easily accessible during play sessions. When your puppy starts to mouth your hands, immediately offer a toy instead. When they engage with the toy, praise them enthusiastically. This teaches them that toys are more rewarding than human skin.
Time-Out Technique
For persistent biters, a brief time-out can be extremely effective. This isn’t punishment in the traditional sense – it’s simply removing your puppy from the exciting situation that’s encouraging the biting behavior. When your puppy bites, calmly say “time-out” and either leave the room yourself or move your puppy to a quiet, safe space for 2-3 minutes.
The key to successful time-outs is timing and consistency. The consequence must happen immediately after the unwanted behavior, and every instance of inappropriate biting should result in the same response. Never use the crate as a time-out space, as this can create negative associations with what should be your puppy’s safe haven.
 Essential Tools and Toys for Bite Training
Essential Tools and Toys for Bite Training
Having the right tools can make your bite training efforts significantly more effective. The goal is to provide your puppy with appropriate outlets for their natural chewing and biting instincts while protecting your hands, furniture, and belongings.
Chew toys should be varied in texture and hardness to keep your puppy interested and address different chewing needs. Rope toys are excellent for puppies who like to tug and pull, while rubber toys can be filled with treats to provide mental stimulation along with chewing satisfaction. Frozen toys can be particularly soothing for teething puppies.
Puzzle toys and treat-dispensing toys serve dual purposes in bite training. They provide appropriate chewing outlets while also engaging your puppy’s mind, helping to tire them out mentally. A tired puppy is generally a better-behaved puppy, making training sessions more effective.
Ian Dunbar, Veterinarian and Dog Trainer: “The secret to successful puppy training isn’t just teaching them what not to do – it’s providing them with plenty of appropriate alternatives. A puppy with access to engaging, appropriate chew toys is far less likely to seek out your hands or furniture for entertainment.”
Rotate toys regularly to maintain your puppy’s interest. What seems exciting on Monday might be boring by Thursday, so having a variety of options and switching them out every few days keeps the novelty factor high. This also prevents your puppy from becoming possessive over specific toys.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Puppy Bite Training
Even well-intentioned dog parents can inadvertently reinforce biting behavior through common training mistakes. Understanding these pitfalls can help you avoid setbacks in your training progress.
Rough play is one of the most common mistakes new puppy owners make. It might seem fun to wrestle with your adorable pup, but this actually teaches them that using their teeth on human skin is acceptable. Instead, focus on structured play with toys that keep their teeth away from your body.
Inconsistency in training approaches can also slow progress significantly. If you allow gentle mouthing sometimes but not others, or if family members have different rules about biting, your puppy will struggle to understand what’s expected. Everyone in the household should follow the same training protocols.
Using punishment or alpha-based training methods can actually make biting worse by increasing fear and anxiety. Techniques like alpha rolls, scruff shaking, or hitting should never be used. These methods can damage the trust between you and your puppy and may escalate into more serious behavioral issues.
Dr. Sophia Yin, Veterinary Behaviorist: “Punishment-based training for puppy biting often backfires because it increases arousal and can actually make the behavior worse. Positive methods that focus on teaching appropriate behavior are not only more humane but also more effective in the long run.”
Waiting too long to address biting behavior is another common mistake. Some owners think their puppy will naturally outgrow the behavior, but without proper guidance, biting can actually intensify as the puppy grows larger and stronger. Start training immediately, even with very young puppies.
Age-Specific Training Strategies
Different ages present different challenges and opportunities in bite training. Understanding your puppy’s developmental stage can help you adjust your approach for maximum effectiveness.
8-12 Weeks: The Foundation Phase
During this crucial period, puppies are most receptive to learning bite inhibition. Their bites are softer and less damaging, making it easier to teach appropriate pressure. Focus on the yelp and withdraw method during this phase, as puppies are naturally attuned to social feedback from their pack.
Socialization is also critical during this period. Expose your puppy to various people, situations, and other well-behaved dogs (after proper vaccinations). This exposure helps them learn appropriate social behaviors and reduces the likelihood of fear-based biting later in life.
3-4 Months: The Teething Challenge
This is often the most challenging phase for bite training, as your puppy’s adult teeth are emerging and they’re experiencing significant discomfort. Provide plenty of appropriate chew toys and consider freezing wet washcloths for additional relief.
During this phase, you may notice an increase in biting intensity. This is normal but requires consistent training responses. Don’t become discouraged if progress seems slow – this is temporary, and maintaining consistency will pay off.
4-6 Months: Refinement and Consistency
By this age, your puppy should be showing significant improvement in bite inhibition. Focus on refining their skills and maintaining consistency in your training approach. This is also an excellent time to introduce more structured training sessions and basic obedience commands.
Karen Pryor, Pioneer of Clicker Training: “The 4-6 month period is when you’ll see the biggest payoff from your early bite inhibition training. Puppies who have received consistent, positive training during their first few months typically show dramatic improvement in their bite control during this phase.”
Addressing Persistent Biting Issues
While most puppies respond well to consistent training, some may require additional strategies or professional help. Understanding when normal puppy behavior crosses into concerning territory is important for every dog owner.
Excessive intensity in biting, where your puppy seems to bite harder over time rather than softer, may indicate the need for professional intervention. Similarly, if your puppy shows signs of guarding behaviors or becomes aggressive when you try to redirect their biting, consulting with a certified dog trainer or veterinary behaviorist is recommended.
Some breeds may require modified approaches to bite training. High-drive working breeds, for example, may need more mental stimulation and structured activities to redirect their natural intensity. Herding breeds might engage in more nipping behavior due to their genetic predisposition to control movement.
Medical issues can sometimes contribute to excessive biting. If your puppy suddenly increases their biting behavior or seems to be in pain while chewing, consult with your veterinarian to rule out dental problems or other health issues.
The Role of Exercise and Mental Stimulation
A tired puppy is a well-behaved puppy, and this is especially true when it comes to biting behavior. Adequate physical exercise and mental stimulation are crucial components of any successful bite training program.
Age-appropriate exercise is key – young puppies shouldn’t engage in intense or prolonged physical activity, but they do need regular opportunities to burn energy. Short play sessions, gentle walks, and interactive games can help reduce the excess energy that often fuels inappropriate biting.
Mental stimulation is equally important and often overlooked. Puzzle toys, training sessions, and scent games can tire your puppy’s mind, making them more likely to rest calmly rather than seek out mischief. Even 10-15 minutes of mental exercise can have a significant impact on your puppy’s behavior.
Dr. Alexandra Horowitz, Canine Cognition Researcher: “Mental stimulation is often more tiring for puppies than physical exercise. A puppy who has engaged their problem-solving skills and worked through challenges is more likely to settle into calm behavior, making training sessions more effective and reducing problematic behaviors like excessive biting.”
Building a Long-Term Training Plan
Successful bite training isn’t just about stopping the immediate behavior – it’s about building a foundation for lifelong good manners and communication with your dog. Creating a structured, long-term training plan helps ensure consistent progress and prevents regression.
Set realistic timelines for your training goals. Most puppies show significant improvement in bite inhibition within 2-4 weeks of consistent training, but complete mastery may take several months. Understanding this timeline helps prevent frustration and keeps you motivated during challenging periods.
Document your progress by keeping a simple training log. Note which techniques work best for your individual puppy, what times of day are most challenging, and what triggers seem to increase biting behavior. This information helps you adjust your approach and identify patterns that might not be obvious day-to-day.
Gradually increase your expectations as your puppy improves. Early in training, you might accept gentle mouthing as progress compared to hard biting. As your puppy develops better control, you can work toward eliminating mouthing behavior entirely in certain situations.
Socialization and Bite Inhibition
Proper socialization plays a crucial role in developing good bite inhibition and overall behavioral health. Puppies who interact appropriately with other dogs and people are more likely to develop excellent bite control and social skills.
Puppy socialization classes provide controlled environments where your pup can learn from other dogs while under professional supervision. These classes often include bite inhibition exercises and give puppies the opportunity to practice their social skills with peers of similar age and energy levels.
Arrange supervised playdates with well-behaved adult dogs who can help teach your puppy appropriate behavior. Adult dogs are often excellent teachers, providing immediate feedback when puppy behavior becomes too rough or inappropriate.
Sue Sternberg, Animal Behaviorist: “Socialization isn’t just about exposure – it’s about creating positive experiences that teach your puppy how to interact appropriately with the world around them. A well-socialized puppy is more confident, less likely to bite out of fear, and generally easier to train in all areas.”
When to Seek Professional Help
While most puppy biting issues can be resolved with consistent home training, some situations warrant professional intervention. Recognizing when to seek help can prevent minor issues from developing into serious behavioral problems.
Contact a certified dog trainer or veterinary behaviorist if your puppy’s biting is getting worse rather than better after several weeks of consistent training. Similarly, if you notice signs of aggression such as growling, stiff body language, or biting that seems intended to cause harm rather than play, professional guidance is essential.
Fear-based biting requires specialized handling and often benefits from professional intervention. If your puppy bites when cornered, handled, or in specific situations, a qualified trainer can help you address the underlying fear while maintaining safety for everyone involved.
Some puppies may have medical issues contributing to their biting behavior. Pain, dental problems, or neurological issues can all influence behavior, so consulting with your veterinarian is important if training efforts aren’t showing expected results.
Success Stories and Realistic Expectations
Every puppy’s journey to bite inhibition is unique, and understanding what success looks like can help you maintain realistic expectations while celebrating progress along the way.
Most puppies show noticeable improvement within the first few weeks of consistent training. You might notice that your puppy’s bites become gentler before they become less frequent – this is normal and shows that they’re learning to control the pressure of their bite.
Some puppies may have setbacks during teething or during adolescence (around 6-18 months). These temporary increases in mouthing or biting behavior are normal and don’t mean your training has failed. Maintain consistency during these phases and the behavior will improve.
Victoria Stillwell, Dog Trainer and TV Host: “Remember that training is a journey, not a destination. The puppy who seemed impossible at 10 weeks old can become the most gentle, well-mannered adult dog with consistent, positive training. Trust the process and celebrate small victories along the way.”
Conclusion: Building a Lifetime of Good Habits
Teaching your puppy to stop biting is one of the most important investments you’ll make in your relationship with your dog. The time and effort you put into bite inhibition training now will pay dividends throughout your dog’s entire life, creating a foundation of trust, communication, and mutual respect.
Remember that every puppy is an individual, and what works perfectly for one might need adjustment for another. Stay patient, remain consistent, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you need it. Your puppy isn’t trying to be difficult – they’re simply learning how to navigate the world around them with your guidance.
The journey from nippy puppy to well-mannered adult dog is filled with challenges, but also with incredible rewards. Every successful training session, every gentle play interaction, and every moment of progress brings you closer to the amazing companion your puppy is destined to become.
Your dedication to proper bite inhibition training not only creates a better-behaved dog but also contributes to a safer, more harmonious relationship between dogs and humans in our communities. Thank you for taking the time to train your puppy properly – your future self, your family, and everyone who meets your well-trained dog will appreciate the effort you’re putting in today.
With patience, consistency, and the right techniques, you’ll successfully teach your puppy that human skin is never an appropriate chew toy, while still preserving their playful, joyful nature. Here’s to many years of gentle play, loving companionship, and the special bond that comes from training built on trust and positive reinforcement.

 Essential Tools and Toys for Bite Training
Essential Tools and Toys for Bite Training